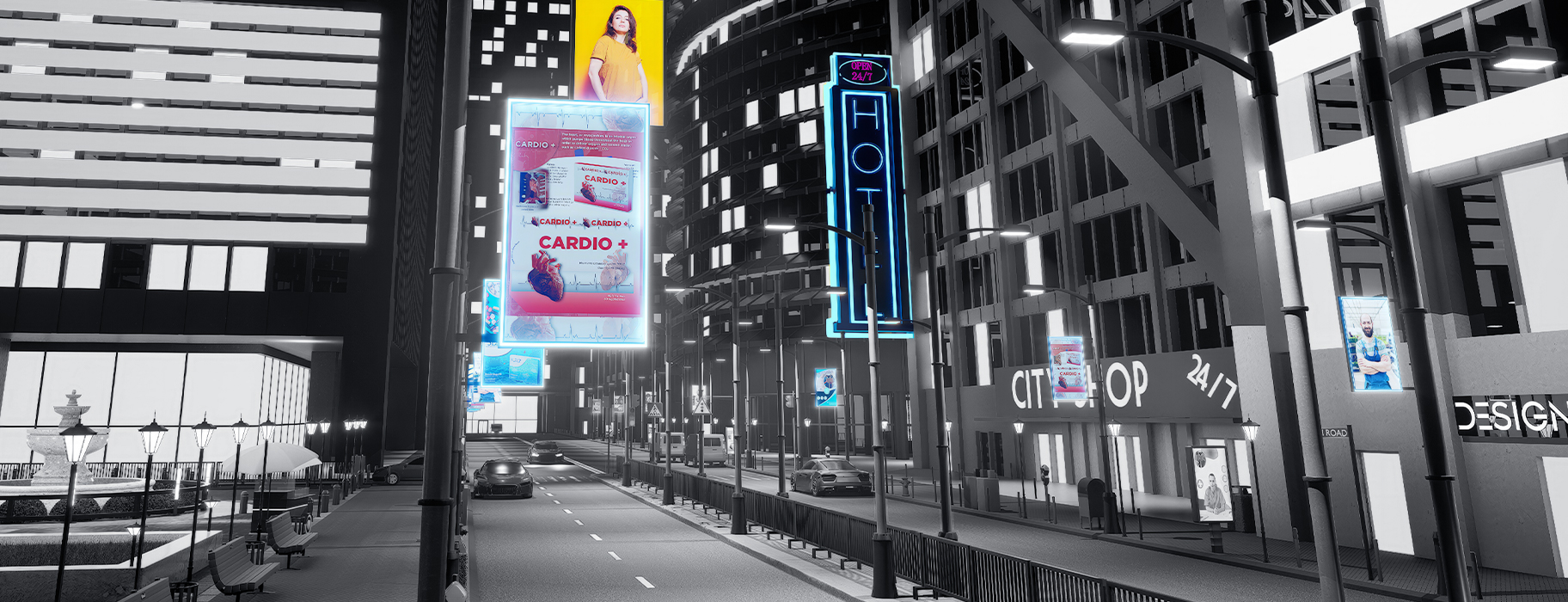
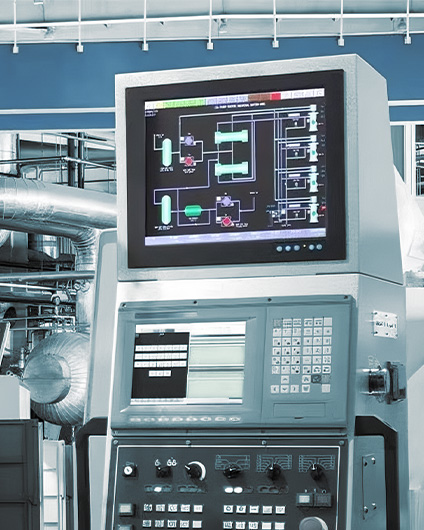
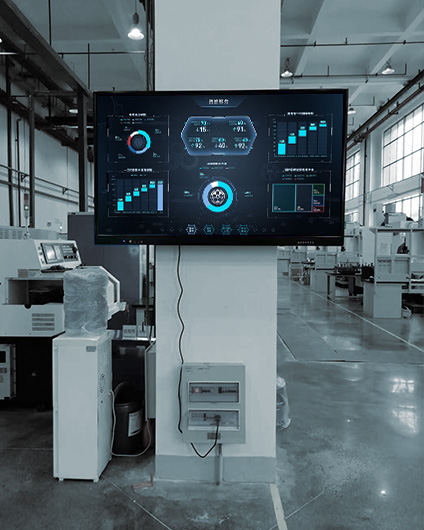
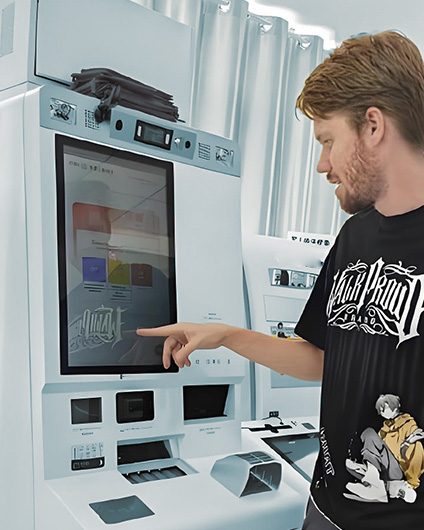
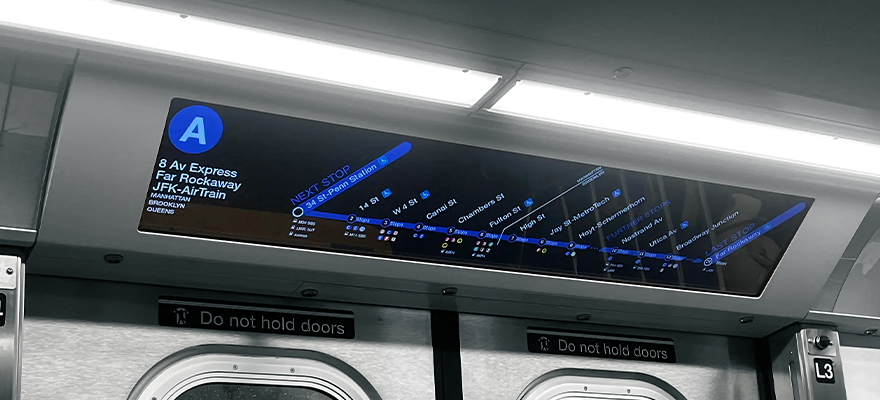
From interactive shop windows in retail stores to real-time information boards in transportation hubs, commercial LCD displays have become indispensable tools in business operations. Digital signage powered by Android motherboards is particularly popular because it combines the flexibility of smartphones with industrial-grade durability, easily integrating various applications.
Android, with its outstanding flexibility, openness, and cost-effectiveness, has become the platform of choice in the commercial display field. This article will delve into network deployment solutions, power supply options, and typical applications of Android digital displays, helping you build a solid technical foundation for your next business project.

What Are The Advantages Of Using Android Motherboards In Commercial Displays?
The choice of an Android motherboard as the core of a commercial display is due to its highly integrated nature. Android motherboards typically have multiple built-in interfaces, such as USB, HDMI, and network ports, enabling seamless connection to peripheral devices. This means the display is not just a screen, but can also function as a smart terminal, handling data acquisition and transmission.
Furthermore, Android motherboards offer robust network support capabilities, compatible with various connection methods from wired to wireless and even mobile networks. This ensures the display remains online in various scenarios, enhancing system reliability and enabling remote updates. This powerful network connectivity lays the foundation for the diverse deployment solutions we will discuss later.

Android Advertising Display Network Deployment Solution
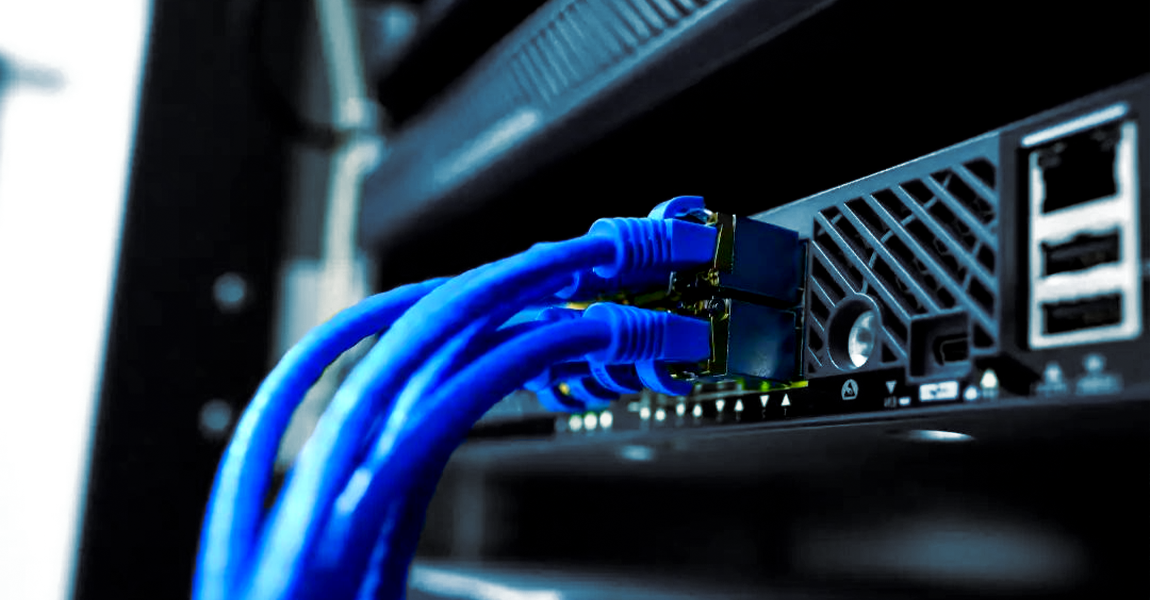
Wired Ethernet
○Advantages: Common wired networks connect directly to switches via RJ-45 interfaces, unaffected by signal interference, with latency typically below 5ms.
For scenarios requiring real-time payments or high-definition live streaming, this stability is unmatched by other solutions.
○Applicable Scenarios: This is the first choice for all fixed installation scenarios, especially retail stores, banks, offices and other occasions that require continuous and stable network connection and online payment or real-time data synchronization.
○Implementation Recommendations: Ensure the motherboard is compatible with gigabit networks and use CAT6 or higher specification network cables to avoid bottlenecks.
In industrial environments, choose shielded twisted pair (STP) cables and provide redundant network ports for easy future expansion or quick replacement.

Wireless Wi-Fi
○Advantages: Wi-Fi offers unparalleled deployment flexibility, eliminating the need for complex network cabling, and allowing devices to easily access local area networks and the internet within wireless signal coverage.
○Challenges: Wi-Fi is relatively unstable and easily affected by environmental factors, such as walls or interference from devices on the same frequency band, posing certain security risks in public network environments.
○Implementation Recommendations: Prioritize Wi-Fi modules that support both 2.4GHz and 5GHz dual-band.
To ensure optimal performance, conduct on-site signal strength measurements and consider using enterprise-grade routers to improve coverage and security.
Cellular Mobile Network
○Advantages: 4G/5G modules provide extensive network coverage, enabling devices to stay online in mobile or remote areas without wired or Wi-Fi connections, which is key to enabling true mobile applications.
○Implementation: Simply insert a 4G/5G internet module into the Mini PCIe or M.2 interface on the motherboard and insert a SIM card to use the operator's network.
○Implementation Recommendations: To address signal fluctuations, an automatic failover mechanism can be configured (e.g., if the main network is wired, automatically switch to 4G/5G in case of failure).
For devices that need to transmit large amounts of data, it is recommended to set up traffic monitoring and alarms to optimize costs.

Bluetooth
○Function: Bluetooth plays a supporting role in network deployment, mainly used for short-range, point-to-point connections with peripheral devices such as printers, barcode scanners, keyboards, and mice.
○Advantages: It features low power consumption, low cost, and easy integration, and can effectively expand device functions to form a complete terminal solution.
○Implementation Recommendations: Bluetooth is typically used in conjunction with the aforementioned Internet access technologies.
When selecting a Bluetooth device, pay attention to the Bluetooth version and its compatibility to ensure stable pairing with the target peripheral device and forming a complete network group.

Power Supply Method For Android Digital Display
AC Power Supply
AC power supply is highly versatile, adaptable to various global voltage standards, from AC100V to 240V, which facilitates easier configuration of display devices in the international market.
AC-powered displays have a built-in power board and require appropriate T-shaped sockets and power cord plugs depending on the region.
When using AC power, local regulations, such as UL or CE certification, must be followed to ensure electrical safety.
DC Power Supply
DC power supply deployment involves using an external adapter to match local power standards and plug types, allowing for flexible input voltage adjustments.
This method is more suitable for specific industrial or mobile scenarios, such as automotive systems or outdoor installations, reducing electromagnetic interference by providing a stable voltage output.
Using DC power supply requires assessing the overall power consumption of the device and ensuring the adapter has sufficient capacity to avoid overload.
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
The advantage of PoE technology is its simplified cabling; a single standard network cable can handle both data transmission and power delivery, reducing installation costs.
This technology is suitable for industrial environments, ceiling-mounted digital signage, or network monitoring displays—scenarios where cabling is difficult or where a minimalist approach is desired.
If using PoE, ensure compatibility with the IEEE 802.3 standard, select a PoE-enabled switch, and use high-quality network cables (such as Cat5e or higher) to maintain stable power supply and transmission.
Android Digital Display Information Publishing Types
Local Playback
Local playback refers to inserting updated content via USB flash drive or TF card.
Content updates are very simple, require no network connection, and are suitable for projects with limited budgets.
Local Area Network (LAN) Publishing
LAN updates are published via Wi-Fi or RJ-45 connection to a computer or media player, serving as an information source.
Its advantage lies in efficient internal management and the ability to quickly synchronize multiple devices.
External Network Publishing
The deployment method for updating content via the external network is also through Wi-Fi or RJ-45, except that the connecting terminal is replaced by a server.
It can be uniformly published using a background manager. The advantage is unified remote control, which facilitates large-scale management.
How To Choose The Best Solution For Your Business Project?
To choose the best solution for your project, simply answer these core questions:
Where will your equipment be installed?
Is it a fixed indoor location, a mobile vehicle environment, or a complex industrial workshop with poor signal coverage? For fixed scenarios, wired connections are preferred; for mobile environments, 4G/5G is essential.
What are your core business requirements?
Does it involve online payments, requiring extremely low network latency and stability? Does it need to operate 24/7? High-demand businesses require diverse network layouts.
How many devices do you need to manage?
Is it a simple application on a single screen, or a nationwide network? Local management at a single point is sufficient; large-scale deployment necessitates a cloud-based communication system.
In short, when choosing a solution, start with your actual pain points, considering your budget and future scalability. If you would like to learn more, please contact us.


![]() Retail Digital Display Solution
Retail Digital Display Solution![]() Public Transportation Digital Signage Solution
Public Transportation Digital Signage Solution![]() Entertainment Digital Display Solution
Entertainment Digital Display Solution![]() Healthcare Digital Display Solutions
Healthcare Digital Display Solutions![]() Education Digital Signage Solutions
Education Digital Signage Solutions![]() Corporate Digital Display Solutions
Corporate Digital Display Solutions![]() Art Digital Display Solution
Art Digital Display Solution![]() Industrial Digital Display Solutions
Industrial Digital Display Solutions![]() Hotel Digital Signage Solutions
Hotel Digital Signage Solutions![]() Outdoor Digital Signage Solutions
Outdoor Digital Signage Solutions